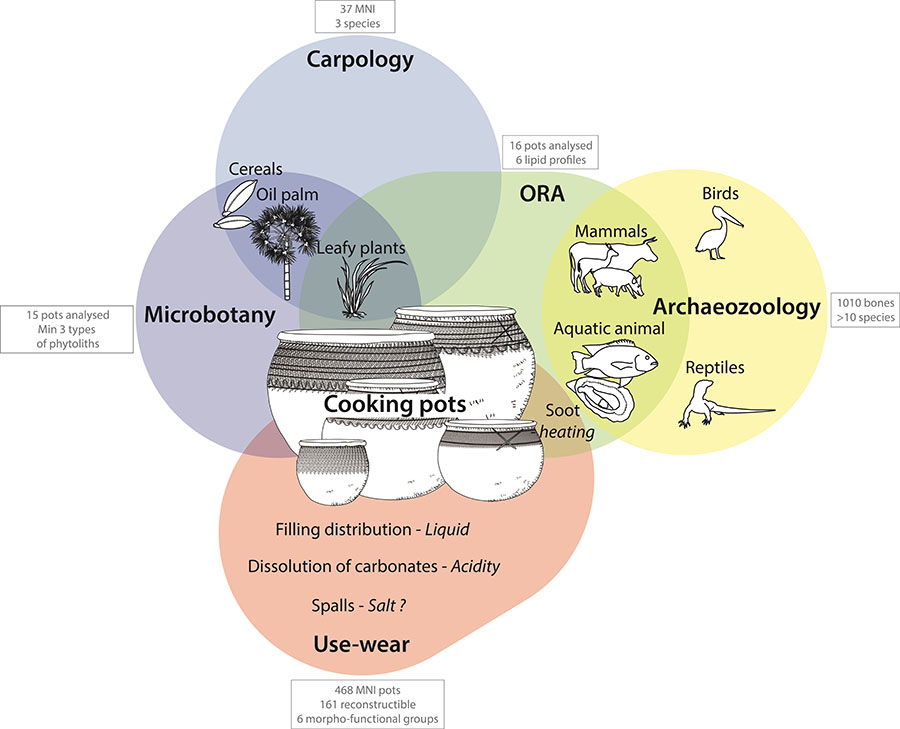
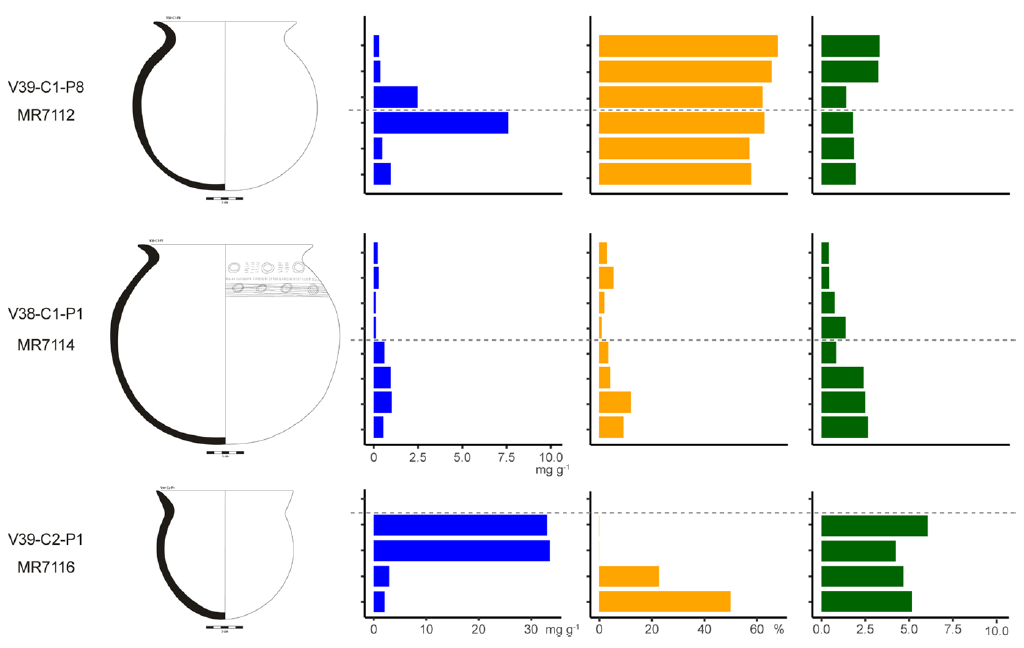
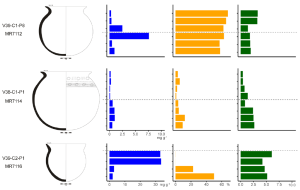
Because they hold information about cultural identity, foodways have been the focus of a variety of disciplines in archaeology. However, each approach documents different stages of culinary preparation and is constrained by the preservation specificities of each type of artefact and ecofact. Difficulties in achieving an interdisciplinary approach may explain the scarcity of such studies. In this paper, we propose a methodology that combines archaeozoological, carpological and microbotanical analysis of ecofacts retrieved in the sediment, with use-alteration, organic residue and microbotanical analysis carried out on pottery vessels, recovered during the excavation of a XXth century archaeological dump site in Lower Casamance (Senegal). The results demonstrate the strength of this multiproxy approach in reconstructing past foodways by characterising the importance of aquatic, terrestrial animals and plant products in the Diola Kassa diet. In addition, this study questions the modalities of food transformation by assessing the preparation techniques of animal and vegetal products (cutting marks, heating processes etc.) and the function of pottery vessels (transport, storage, cooking etc.). Aquatic products and rice were a significant part of the diet of the users of the dump (from archaeozoology, carpology, phytoliths and organic residue analysis) and wet cooking (boiling?), salty and acidic foods seem to have been particularly prevalent (from use-alteration). The absence of specific animal and plant parts in the archaeological record, as well as some pottery function, is also questioned. Beyond gathering the results of each approach, this study focuses on the interweaving of different research methods to depict past foodscape.
Article en open access : https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295794
Projet : Foodways in West Africa (Sinergia)